Key Takeaways
Nicotine leaves the body quickly, but its metabolite lasts much longer: Nicotine itself is usually eliminated within 1–3 days, but cotinine (the primary metabolite tested for) can remain detectable for up to 10 days in blood and up to 3 weeks or longer in urine for heavy users.
Detection time varies by test type and individual factors: Nicotine and cotinine can be detected for different lengths of time depending on whether testing is done via blood, urine, saliva, hair, or breath, as well as factors like metabolism, age, genetics, body fat, liver health, and frequency of use.
Vaping and nicotine pouches can prolong exposure: Because vaping and products like Zyn allow more frequent, discreet use, they can lead to constant nicotine intake, higher tolerance, and longer detection times compared to traditional cigarette smoking.
Nicotine content differs widely by product: Cigarettes contain about 10–15 mg of nicotine each (with 1–2 mg absorbed), while vape liquids and pouches vary significantly in strength, which directly affects how much nicotine builds up in the system.
Stopping nicotine use is the only reliable way to clear it: Hydration, exercise, and a healthy diet may support metabolism, but the most effective way to remove nicotine and cotinine from the body is to stop using nicotine products and allow time for natural elimination.
The question of “how long does nicotine stay in your system” depends on method of consumption, as well as whether we are talking about nicotine, the active substance, is felt in your system, or whether we are talking about how many days out from use its metabolites can be detected on drug tests. This article will answer all that.
Several factors affect how long nicotine and its metabolites remain detectable in the body, including nicotine half-life, the type of nicotine product used, frequency of use, and individual biological differences.
What Is Nicotine?
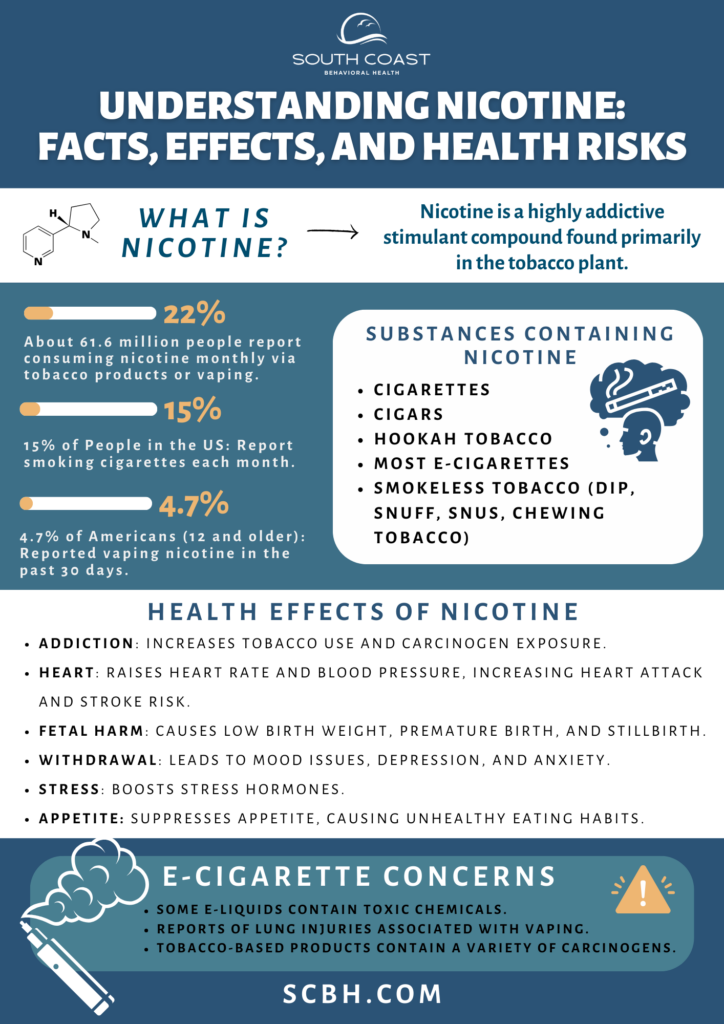
Nicotine is a highly addictive substance and stimulant compound found primarily in the tobacco plant (Nicotiana tabacum). It is also present in smaller amounts in nightshades. Nicotine is the main addictive substance in both tobacco and vaping products, used for the pleasurable and calming feelings it produces in the brain. Over time, the brain craves these effects, leading to regular use and, for many, addiction.
People mainly consume nicotine through traditional cigarettes and other tobacco-based products, as well as vaping. Traditional cigarettes and tobacco smoke are primary sources of nicotine exposure. Tobacco smoke contains harmful chemicals such as tar and other toxic substances that can damage the lungs and heart. Vaping products may also contain harmful chemicals, though the composition can vary. The nicotine content varies between products, affecting how much nicotine is absorbed and detected in the body.
Here are some quick nicotine facts:
Per the National Institute on Drug Abuse, 22% of the US population (about 61.6 million people) report consuming nicotine in some form (whether via tobacco products or vaping) on a monthly basis.
More than 15% of people in the US report smoking cigarettes each month, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
According to the 2023 National Survey on Drug Use and Health, among Americans 12 and older, 4.7% reported vaping nicotine in the past 30 days.
Approximately 49 million Americans consuming nicotine in each year and 1.25 billion worldwide, according to the World Health Organization.
Nicotine use is associated with several health risks, including addiction, increased heart rate, and high blood pressure. In addition to nicotine, tobacco smoke and vaping products contain harmful chemicals that contribute to health risks beyond nicotine itself.
When it comes to how long does nicotine stay in your system, it’s important to note that it’s not just about the nicotine itself, but also its metabolite, cotinine. Nicotine is broken down by the liver into several byproducts, primarily cotinine. This remains in the body far longer than nicotine and thus is important to keep in mind when it comes to drug tests.
What Substances Contain Nicotine?
All tobacco products contain nicotine, including cigarettes, cigars, smokeless tobacco (such as dip, snuff, snus, and chewing tobacco), hookah tobacco, and most e-cigarettes. Nicotine replacement products, such as patches and gum, also contain nicotine and can contribute to its presence in the body.
How Much Nicotine Is in a Vape?
Standard vape products are available in a range of nicotine levels, with commercial vape juice offered in concentrations of 0 mg, 3 mg, 6 mg, 12 mg, and 18 mg per milliliter. For consumers with a higher tolerance level, high-dose cartridges with 24-36 milligrams per milliliter are also available.
How Much Nicotine Is in a Cigarette?
The nicotine content of traditional cigarettes averages about 10-15 mg per cigarette, but smokers typically absorb only about 1-2 mg of nicotine from each traditional cigarette.
Get confidential help from our addiction treatment specialists in Orange County. Call to join our rehab program today!
Call 866-881-1184Is Nicotine Bad for You?
While it’s not the primary cause of diseases associated with smoking (such as lung cancer, emphysema, or cardiovascular disease), nicotine does have various health effects on its own:
Nicotine is highly addictive. Some have argued it is the most addictive drug. This addiction can lead to increased consumption of tobacco products, which exposes users to harmful carcinogens and other toxic compounds. Tobacco smoke contains nicotine, cotinine, and other related substances, many of which are harmful chemicals.
Nicotine increases heart rate and blood pressure. Chronic exposure can contribute to the hardening of arterial walls, potentially increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
There’s evidence that nicotine can harm fetal development, leading to low birth weight, premature birth, and stillbirth. Pregnant individuals are strongly advised to avoid nicotine.
Nicotine withdrawal can cause mood disturbances, depression, and anxiety. After quitting nicotine, individuals often experience physical symptoms and physical withdrawal symptoms such as cravings, irritability, headaches, and discomfort, which typically peak within the first week and gradually diminish. However, the mental and emotional effects of nicotine withdrawal, including anxiety and mood changes, can persist for several months and may require medical support, especially for those with pre-existing mental health conditions.
Nicotine can increase the release of stress hormones.
Some people use nicotine for its appetite-suppressing effects. This can lead to an unhealthy relationship with food.
Because nicotine is a stimulant, it can disrupt sleep. The research on nicotine and sleep shows that prolonged nicotine use is linked to poor sleep quality, as well as sleep disorders.
Some have argued nicotine is a gateway drug, and thus can open the door to usage of harder drugs down the line.
Nicotine can be detected in urine, blood, saliva, hair, and nails after tobacco use. Cotinine, the primary nicotine breakdown product, is commonly tested for in nicotine screening tests, along with other related substances, because it remains in the body longer than nicotine itself. Genetics can affect how quickly an individual metabolizes nicotine, leading to differences in how long nicotine and its byproducts stay in the system.
In addition, it should be noted that, while often marketed as a safer alternative to smoking, e-cigarettes introduce their own set of concerns. For instance, some e-liquids have been found to contain toxic chemicals, and there have been reports of lung injuries associated with vaping.
And, of course, any tobacco-based product will contain a variety of carcinogens, especially cigarettes. Cigars and pipes also contain carcinogens, albeit to a somewhat lesser extent than cigarettes, which contain many additives.
How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Your System?
The length of time nicotine and its metabolites such as cotinine stay in your system can depend on numerous factors. Various factors affect how long nicotine and its metabolites remain detectable, including the type of nicotine product used, frequency of use, individual biological differences, and the specific test used to detect it. Nicotine leaves the body at different rates depending on these factors, and nicotine levels can be measured through blood, urine, saliva, hair, and breath tests.
Blood — Nicotine can usually be detected in the blood for one to three days after consuming tobacco or nicotine products. Cotinine, a primary metabolite of nicotine, can be detected in the blood for up to ten days in heavy users and is often tested for in nicotine screening tests because it remains in the body longer than nicotine itself.
Urine — Nicotine itself may be detected in urine for up to three days, while cotinine can be detected for up to three weeks or longer, depending on factors like the individual’s metabolism, hydration level, and tobacco usage. Heavy or chronic users accumulate higher levels of cotinine, detectable for up to 3 weeks, while occasional users have levels detectable for approximately 4 days.
Saliva — Nicotine may be detectable in saliva for up to four days.
Hair — Hair testing is the most reliable for long-term detection and can detect nicotine for up to one to three months after exposure. In some cases, especially with chronic exposure, it might be detectable for up to 12 months.
Breath — Breath tests can detect nicotine for up to 24 hours after ingestion.
High body fat may increase nicotine’s detection time due to storage in fatty tissues. Physical activity and hydration can influence nicotine metabolism and elimination rates. Genetic variations in the CYP2A6 enzyme affect how quickly nicotine is metabolized, with some individuals processing it more slowly. Older adults (over 65) process nicotine more slowly, clearing it up to 23% slower than younger adults, while women generally metabolize nicotine faster than men, especially during pregnancy due to estrogen. The health of your liver and kidneys is also crucial for processing and eliminating nicotine.
Withdrawal symptoms from nicotine typically peak at around 3 days after cessation and are most intense within the first week. Common nicotine withdrawal symptoms include cravings, irritability, and anxiety. Many physical withdrawal symptoms improve within a few weeks after quitting, but cravings can persist for months. Managing cravings is an important part of withdrawal support and relapse prevention.
Some commercial products and herbal remedies claim to speed up the body’s ability to clear nicotine, but they are not usually scientifically tested. Drinking plenty of water, eating a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and exercising may help speed up the detoxification process by improving circulation and metabolism.
Remember, these are general estimates, and the actual detection time can vary based on multiple factors. Additionally, individuals who use tobacco or nicotine products regularly will likely have detectable levels for longer periods compared to occasional users.
If you’re trying to quit smoking or using nicotine products, consider reaching out to medical professionals or support groups for guidance and resources.
How Long Does Vape Nicotine Stay in Your System?
This is somewhat difficult to answer. The elimination half-life of nicotine, whether from vaping or regular smoking, is typically around two hours. This means that it takes the body roughly two hours to eliminate nicotine from its system.
However, the nicotine content in vape products can vary widely, which contributes to differences in how long nicotine stays in the system. Additionally, nicotine is broken down into several byproducts, primarily cotinine, by the liver, and both nicotine and cotinine are used in testing to determine recent use of nicotine products.
Nicotine consumption via tobacco smoking has almost a built-in limit, because most people do not smoke indoors — the need to go outside imposes “friction” on one’s ability to consume nicotine. Because of this, nicotine consumption via smoking is intermittent.
But vaping leaves no odor, and there are fewer restrictions on its use indoors, so the consumption of nicotine is far more constant, with some people using it up to 24 hours a day. As a result, tolerance builds far faster, leading to nicotine consumption that ensures the substance stays in the body far longer. This can make quitting vaping very difficult.
How Long Does Zyn Nicotine Stay in Your System?
Again, this is difficult to answer. Some people try to use nicotine pouches like Zyn to quit smoking, but it’s important to compare them to nicotine replacement products such as patches or gum. Both deliver nicotine, but nicotine pouches often have a different nicotine content and can be used more discreetly, potentially leading to more frequent dosing. Unlike nicotine replacement products, which are designed to help manage withdrawal with controlled nicotine content, pouches can result in a constant inflow of nicotine into the body. Upon ceasing use, nicotine is broken down by the liver into several byproducts, primarily cotinine. It will take one to three days for Zyn withdrawal to conclude and for the nicotine to leave your system; up to ten days for cotinine.
How Long is Zyn Withdrawal?
Zyn withdrawal follows the same general pattern as withdrawal from other nicotine products, though symptoms can feel more intense for some users due to the frequent dosing common with nicotine pouches. Withdrawal symptoms usually begin within the first 24 hours after stopping use and tend to peak around days two to three. During this time, individuals may experience strong cravings, irritability, headaches, anxiety, and difficulty concentrating. Over the next one to two weeks, physical symptoms typically begin to subside, although cravings may still occur. Most physical withdrawal symptoms resolve within three to four weeks, but psychological cravings can persist for several months, particularly in people who used Zyn consistently throughout the day. Support through behavioral therapy, nicotine replacement options, or medical guidance can make the withdrawal process more manageable and reduce the risk of relapse.
How to Clear Nicotine From Your System
The best way to do this is first and foremost to stop using nicotine.
Aside from that, you can support your body’s metabolic processes, such as to drink plenty of water, exercise a couple times week, and eat a healthy diet.
Looking for quality substance abuse treatment that’s also affordable? South Coast accepts most major insurance providers. Get a free insurance benefits check now.
Check Your CoverageQuitting nicotine involves understanding how nicotine enters the body and how it affects how long nicotine stays in your system. Whether through smoking and vaping, nicotine quickly enters the body, and healthcare professionals can help monitor levels of nicotine and testing for nicotine to track progress. For heavy smokers with nicotine dependency, nicotine replacement therapies can help remove nicotine from your body and ease nicotine withdrawal symptoms by helping the body break down nicotine and metabolize nicotine more efficiently. Over time, these strategies reduce traces of nicotine and lower nicotine exposure, while guidance on secondhand smoke and overall smoking cessationsupports your goal to stop smoking and keep nicotine from reentering the body.
Detection and Testing for Nicotine
Understanding how to detect nicotine in your system is an important step for anyone looking to quit smoking, manage nicotine withdrawal symptoms, or monitor exposure to secondhand smoke. Nicotine tests are commonly used in healthcare settings, workplaces, and even for personal monitoring, as they can reveal recent nicotine use or ongoing exposure to tobacco products.
There are several types of nicotine tests, each with its own detection window and method. Urine tests are the most frequently used, as they can detect nicotine and its primary byproduct, cotinine, for up to three weeks after the last use. This makes urine testing a reliable option for tracking nicotine exposure over time. Blood tests offer a shorter detection window, typically up to 10 days, but can provide more immediate results about recent nicotine use. Saliva tests are non-invasive and can detect nicotine for up to four days, making them useful for quick screenings. For those interested in long-term patterns of nicotine use, hair testing can reveal nicotine exposure for several months, which is especially helpful in monitoring chronic users or assessing secondhand smoke exposure.
If you’re using nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) products, such as nicotine patches or gum, it’s important to know that these can also result in positive nicotine test results. However, the amount of nicotine delivered by NRT products is generally much lower than what’s found in traditional tobacco products. This controlled delivery helps manage withdrawal symptoms while reducing overall nicotine dependence, supporting your journey to quit smoking.
Managing nicotine withdrawal symptoms is a key part of the quitting process. Strategies like drinking plenty of water, eating a balanced diet, and engaging in regular exercise can help boost your metabolism and remove nicotine from your system more efficiently. Avoiding triggers—such as environments where you used to smoke or drinking alcohol—can also make it easier to stick to your quit plan and handle withdrawal symptoms.
For those struggling with nicotine dependence, smoking cessation programs offer structured support. The National Cancer Institute recommends combining behavioral therapies with NRT products for the most effective results. These programs can help you manage both the physical and mental aspects of withdrawal, providing tools and support to help you quit tobacco for good.
When it comes to testing, it’s not just about detecting nicotine itself. Cotinine tests are often used because cotinine, a byproduct of nicotine, stays in the body much longer—up to 10 days or more. Cotinine levels can vary based on several factors, including your body weight, how much nicotine you use, and your overall tobacco use habits. This makes cotinine testing a more accurate way to measure nicotine exposure, whether from direct use or secondhand smoke.
Ultimately, understanding how long nicotine stays in your system and how it can be detected is essential for anyone looking to quit tobacco or nicotine products, manage withdrawal symptoms, or monitor nicotine exposure. By learning about the different types of nicotine tests, how NRT products affect test results, and practical ways to boost metabolism and remove nicotine, you can take meaningful steps toward a healthier life.
Addiction Treatment at South Coast Behavioral Health
For those struggling with nicotine addiction, South Coast Behavioral Health offers compassionate and affordable addiction treatment.
The first step is going through a medical detox. Our medical detox program in California is staffed by caring and compassionate professionals who can provide you with medications to manage your withdrawal symptoms.
At South Coast, we take pride in offering care that is closely tailored to specific issues. To that end, we offer gender-specific detox programs, with medical detox for men in Irvine, CA, and medical detox for women in Huntington Beach, CA.
After detoxing, proper treatment can begin.
Treatment for substance abuse takes place along an entire spectrum of care. Along that entire spectrum are various behavioral therapies, support groups, and the use of medically-assisted treatment (MAT).
These levels of treatment are, in order, as follows:
Residential Treatment in California
After successfully completing medical detox, you’ll move to inpatient treatment in Orange County, California. There, you’ll receive medically-assisted treatment and dual diagnosis treatment to deal with any cravings or co-occurring mental health issues you may be battling. We also offer residential treatment facilities in Costa Mesa, Irvine, and Huntington Beach for those who desire gender-specific treatment. There, patients get round-the-clock medical attention and monitoring while living at our facility full-time.
In addition to individual and group counseling and medication management, you’ll also have access to leisure activities and family support services.
Partial Hospitalization in California
Most patients start substance abuse treatment with South Coast in our residential treatment program. After completing that, many desire something that still provides structure and support but with extra space and time to oneself. For that, we offer Partial Hospitalization in Newport Beach.
A step down from inpatient care but with more structure than conventional outpatient programs, partial hospitalization offers a good balance for those looking to ease back into normal life. patients can receive care five to seven days a week for a number of hours each day, returning back to their sober living homes in the evening.
This way, they can recover without putting their daily lives completely on hold, receiving intense therapeutic interventions like group and individual therapy, skills development, and medication management as necessary.
Intensive Outpatient Treatment in California
For those leaving inpatient residential treatment or partial hospitalization, intensive outpatient programs (IOP) are yet another gradual step forward on the road to recovery.
With a focus on group therapy, individual counseling, and education, patients undergoing Intensive Outpatient Treatment in Newport Beach can meet three to five days a week. Each session lasts three hours.
This level of care requires the least amount of attendance at a facility. It’s also most likely the best option for treating nicotine addiction for most people, along with support groups.
Get Started Today
If you or a loved one are struggling with nicotine addiction but wonder how long addiction counseling takes or have other questions, call us at 866-881-1184 or contact us here. Our highly qualified staff will be happy to help give you an idea regarding how long does nicotine stay in your system, what to expect from your addiction recovery timeline, help verify your insurance, and assist with any other questions you may have.
How long does nicotine stay in your system?
How long does vape stay in your system?
How long does cotinine stay in your system?
- 2023 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) Releases | CBHSQ Data
- Tobacco Use – Health, United States
- What is the scope of tobacco, nicotine, and e-cigarette use in the United States? | National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)
- E-cigarette, or Vaping Product, Use Associated Lung Injury (EVALI) > Fact Sheets > Yale Medicine
- Effects of Nicotine on the Central Nervous System and Sleep Quality in Relation to Other Stimulants: A Narrative Review – PMC
- Effects of Nicotine During Pregnancy: Human and Experimental Evidence – PMC
- Tobacco use declines despite tobacco industry efforts to jeopardize progress
Author
-
Content Writer
Pierce Willans is a professional writer and editor specializing in substance abuse and addiction treatment. Having written everything from informational articles to landing page copy, he now seeks to bring his years of experience to his current role at South Coast Behavioral Health. He's passionate about educating people on the dangers of drug abuse and the importance of addiction treatment, with a personal interest in how various substances affect brain chemistry. In his free time, he enjoys reading, writing, and pursuing a healthy lifestyle. Pierce continues to refine his approach to making addiction-related information accessible and available to all.
View all posts








